Hey there, tech enthusiasts! Ever wondered about the mysterious world of NetBIOS domain names? Well, wonder no more because we’re about to dive deep into the fascinating realm of NetBIOS domain names and unravel their secrets. So, buckle up and get ready to expand your knowledge!
In the vast landscape of computer networking, NetBIOS domain names play a vital role. But what exactly are they? NetBIOS, short for Network Basic Input/Output System, is a protocol that allows computers to communicate with each other on a local area network (LAN). Think of it as the language that computers use to talk to one another. Now, within this NetBIOS world, domain names serve as unique identifiers for groups of computers.
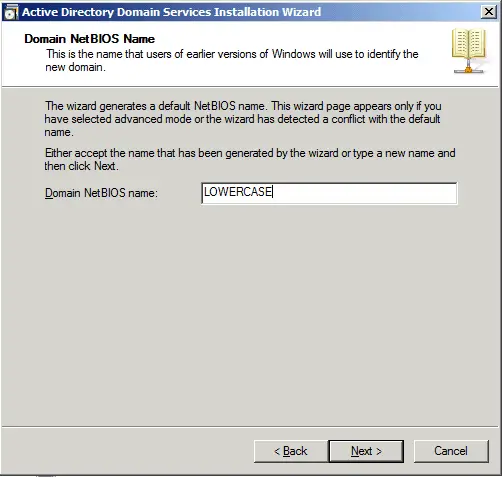
Understanding NetBIOS domain names is like deciphering a secret code. They consist of up to 15 characters and can contain letters, numbers, and a few special characters. These names are used to represent a specific network or workgroup, providing a sense of organization and structure. Whether you’re a networking newbie or a seasoned pro, grasping the concept of NetBIOS domain names is essential for navigating the intricacies of computer networks. So, let’s embark on this journey together and demystify the world of NetBIOS domain names!
Understanding NetBIOS Domain Names
NetBIOS (Network Basic Input/Output System) domain names play a crucial role in computer networking. They are used to identify and locate resources on a network, such as computers, printers, and shared folders. In this article, we will delve into the details of NetBIOS domain names, their significance, and how they function in a network environment.
What is NetBIOS?
NetBIOS is a protocol developed by IBM and Microsoft in the 1980s to facilitate communication between computers within a local area network (LAN). It provides a set of services for naming, session establishment, and message transfer. NetBIOS was widely used in early LANs but has been largely replaced by more modern protocols like TCP/IP.
NetBIOS names are 16 characters long and are used to identify network resources. Each resource within a network must have a unique NetBIOS name. These names are not case-sensitive and can contain letters, numbers, and certain special characters.
NetBIOS Domain Names vs. Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs)
While NetBIOS domain names are widely used in older networks, modern networks often rely on Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) for resource identification. FQDNs are based on the Domain Name System (DNS) and provide a hierarchical naming structure.
Unlike NetBIOS domain names, FQDNs are globally unique and can be resolved to IP addresses. They are composed of multiple levels, such as the host name, domain name, and top-level domain. FQDNs are essential for internet connectivity and are commonly used in enterprise networks.
Benefits of NetBIOS Domain Names
NetBIOS domain names still have their merits in certain network environments. Here are some benefits of using NetBIOS domain names:
1. Simplicity: NetBIOS names are shorter and easier to remember compared to FQDNs, making them more user-friendly in small, local networks.
2. Legacy Support: Many legacy applications and operating systems rely on NetBIOS names for resource identification and network communication. Using NetBIOS domain names allows compatibility with such systems.
3. Seamless Integration: NetBIOS domain names can coexist with FQDNs in a network, providing flexibility and compatibility between different naming systems.
How NetBIOS Domain Names Work
NetBIOS domain names are used in conjunction with the NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) protocol. When a computer wants to communicate with another resource on the network, it sends out a NetBIOS name query broadcast to the local network segment.
The NetBIOS name query broadcast is received by all computers on the local network segment. The computer with the requested NetBIOS name responds with its IP address, allowing the initiating computer to establish a connection.
NetBIOS Name Resolution Methods
There are several methods for resolving NetBIOS names to IP addresses:
1. Local Name Cache: Each computer maintains a local name cache that stores recently resolved NetBIOS names and their corresponding IP addresses. When a name is requested, the computer first checks its cache for a match before broadcasting a query.
2. WINS (Windows Internet Name Service): WINS is a central name resolution service used in Windows networks. It maintains a database of NetBIOS names and their corresponding IP addresses. When a name query is broadcast, computers can consult the WINS server for resolution.
3. Broadcast Resolution: If the local cache and WINS do not yield a match, a name query is broadcast to the local network segment. The computer with the matching NetBIOS name responds directly, providing its IP address.
NetBIOS Domain Names in Modern Networks
While NetBIOS domain names were prevalent in earlier network architectures, modern networks have shifted towards other naming systems like DNS and Active Directory. These newer systems offer enhanced scalability, security, and integration with the internet.
However, NetBIOS domain names are still relevant in certain scenarios, such as legacy systems or small local networks. Understanding the basics of NetBIOS domain names can help network administrators navigate mixed network environments and ensure seamless communication between resources.
The Importance of NetBIOS Domain Names
NetBIOS domain names serve a crucial role in computer networking, especially in legacy systems. They provide a simple and efficient way to identify and locate network resources, allowing for seamless communication within a local network. While the use of NetBIOS domain names has decreased in modern networks, they still have their place in certain environments.
NetBIOS vs. DNS: A Comparison
When comparing NetBIOS domain names to the Domain Name System (DNS), there are several key differences to consider. NetBIOS domain names are generally limited to the local network, while DNS allows for global resolution of domain names to IP addresses. DNS also offers a hierarchical naming structure, enabling the organization of resources in a more organized and scalable manner.
Furthermore, NetBIOS domain names rely on broadcasts and local name caches for resolution, while DNS utilizes a distributed system of servers for efficient and reliable name resolution. DNS also supports additional features such as security mechanisms like DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) and dynamic updates.
Benefits of NetBIOS Domain Names
Although NetBIOS domain names have become less prevalent in modern networks, they still offer certain advantages in specific situations:
1. Compatibility: NetBIOS domain names are widely supported by legacy systems, ensuring seamless integration with older network infrastructure and applications.
2. Simplicity: NetBIOS names are shorter and easier to remember than their DNS counterparts, making them more user-friendly in small, localized networks.
3. Flexibility: NetBIOS domain names can coexist with DNS names in a network, providing compatibility and flexibility between different naming systems.
Limitations of NetBIOS Domain Names
Despite their benefits, NetBIOS domain names also have some limitations:
1. Scalability: NetBIOS was designed for small, localized networks, and it may not scale well in larger enterprise environments. DNS is better suited for managing large networks with thousands of resources.
2. Security: NetBIOS lacks robust security features compared to DNS. DNSSEC, for example, provides cryptographic signatures to verify the authenticity and integrity of DNS data.
3. Internet Compatibility: NetBIOS domain names are not compatible with the internet, as they are not globally unique or resolvable outside of the local network.
In conclusion, while NetBIOS domain names have their advantages, they are gradually being replaced by more modern naming systems like DNS. However, understanding NetBIOS domain names is still important for network administrators working with legacy systems or small, localized networks.
Key Takeaways: Understanding NetBIOS Domain Names
- NetBIOS is a protocol used for communication between computers on a local network.
- Domain names in NetBIOS are used to identify and locate resources on a network.
- NetBIOS domain names are limited to 15 characters and can include letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Each computer on a network needs a unique NetBIOS name to avoid conflicts.
- NetBIOS domain names are different from DNS domain names used on the internet.
Frequently Asked Questions
NetBIOS domain names play a crucial role in computer networking, particularly in Windows-based environments. Understanding how they work is essential for managing and troubleshooting network resources effectively. In this section, we address some common questions about NetBIOS domain names.
1. What is a NetBIOS domain name?
A NetBIOS domain name is a unique identifier used to identify and manage resources within a Microsoft Windows network. It is a string of up to 15 characters that helps distinguish one network from another. NetBIOS domain names are often used in conjunction with IP addresses to facilitate communication between computers.
In a Windows-based network, each computer is assigned a NetBIOS name, which is then combined with the domain name to create a fully qualified domain name (FQDN). This FQDN is used to locate and access network resources.
2. How are NetBIOS domain names resolved?
NetBIOS name resolution is the process of translating a NetBIOS name into an IP address. There are two methods commonly used for NetBIOS name resolution:
– Broadcast: In this method, the computer sends out a broadcast message to the network, asking for the IP address associated with a specific NetBIOS name. The computer with the matching name responds with its IP address.
– WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service): WINS is a centralized database that stores NetBIOS name-to-IP address mappings. When a computer needs to resolve a NetBIOS name, it queries the WINS server for the associated IP address.
3. Can NetBIOS domain names be changed?
Yes, NetBIOS domain names can be changed, but it is not a straightforward process. Changing the domain name requires careful planning and execution to ensure minimal disruption to network resources and services. It typically involves updating DNS records, Active Directory configurations, and reconfiguring network devices.
Before changing a NetBIOS domain name, it is crucial to thoroughly assess the impact on existing applications, services, and dependencies. It is recommended to consult with network administrators or IT professionals experienced in domain name changes.
4. What are the limitations of NetBIOS domain names?
NetBIOS domain names have certain limitations that network administrators should be aware of:
– Length: NetBIOS domain names can only be up to 15 characters long, which may impose restrictions on choosing descriptive or easily recognizable names.
– Case-insensitive: NetBIOS domain names are not case-sensitive, meaning that “example” and “EXAMPLE” would be considered the same name. This can lead to confusion and potential conflicts.
– Compatibility: NetBIOS domain names are primarily used in Windows-based environments and may not be compatible with non-Windows systems or newer networking technologies.
5. How do NetBIOS domain names differ from DNS domain names?
NetBIOS domain names and DNS domain names serve different purposes in network infrastructure:
– NetBIOS domain names are used for local network identification and resource access within Windows-based environments. They rely on NetBIOS protocols for name resolution and communication.
– DNS domain names, on the other hand, are used for global network identification and resource access across different platforms and operating systems. DNS relies on hierarchical naming structures and the Domain Name System (DNS) for name resolution.
While NetBIOS domain names and DNS domain names can coexist, there is a growing trend towards using DNS as the primary method for name resolution and domain management in modern network architectures.
Understanding concept of NETBIOS and NETBIOS enumeration
Final Summary: Understanding NetBIOS Domain Names
So there you have it, a comprehensive guide to understanding NetBIOS domain names! We’ve covered the basics of what NetBIOS is and how it functions, as well as the significance of domain names in this context. NetBIOS domain names play a crucial role in identifying and organizing resources in a network, making it easier for computers to communicate and share information. By grasping the fundamentals of NetBIOS domain names, you can navigate the world of networking with confidence and efficiency.
As we conclude our exploration of NetBIOS domain names, it’s important to remember the importance of optimizing your network for search engines. Just as we strive to make our articles rank high on Google, it’s crucial to ensure that your network is easily discoverable by other devices. By incorporating relevant keywords and following on-page optimization best practices, you can enhance the visibility and accessibility of your NetBIOS domain names. Remember, a well-optimized network is like a well-oiled machine, operating smoothly and efficiently.
So go ahead and apply your newfound knowledge of NetBIOS domain names, and watch your network thrive. Whether you’re a networking enthusiast or a professional in the field, understanding the intricacies of NetBIOS domain names is a valuable asset. Embrace the power of NetBIOS, optimize your network for search engines, and unlock a world of seamless communication and collaboration. Happy networking!